a). Deformable mirror open loop control:
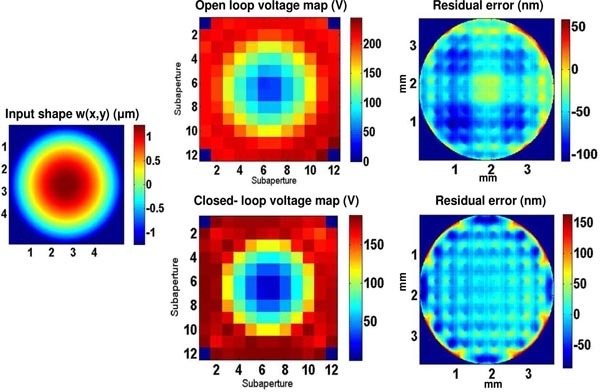
I characterize the errors associated with open-loop control of a MEMS deformable mirror using an approach that combines sparse calibration of the electrostatic actuator state space with an elastic plate model of the mirror facesheet. The sources of measurement error and modeling error are quantified. It is demonstrated that the DM can be shaped in a single step to a tolerance of ∼8 nm of that achievable with iterative feedback-based closed-loop control. Zernike polynomials with up to 2.5 μm amplitude were made with this approach and yielded a shape error of <25 nm rms in most cases. Residual errors were shown to be due primarily to spatial resolution limits inherent in the DM (e.g., uncontrollable errors).
b). Manufacturing technology development for MEMS optical components:
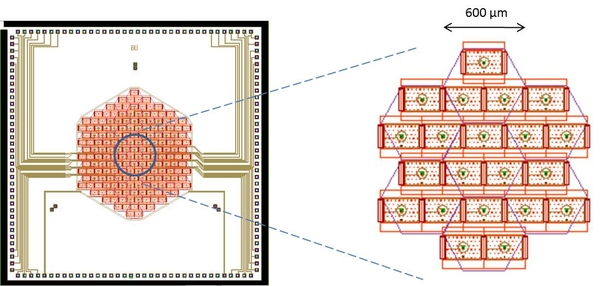
One example showing a tip-tilt-piston MEMS DM which has a 1µm stroke @ 50kHz. Potentially good for sweep laser cavity.